
Travelers should be aware of the potential hazards associated with scuba diving, especially when traveling to the tropics or developing nations to dive. Millions of people travel out of their home countries each year to dive.

#BAROTRAUMA LUNGS PROFESSIONAL#
Travelers should only dive with an operator certified by the Professional Association of Diving Instructors (PADI).Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) ventilatory induced lung injury (VILI) inspiratory volume (IV) barotrauma acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) lung edema.

The blood could contain some mediators which attenuate the damage induced by barotrauma We concluded that an optimal PEEP exists, which protects against barotrauma, however, excess of PEEP could enhance its development.

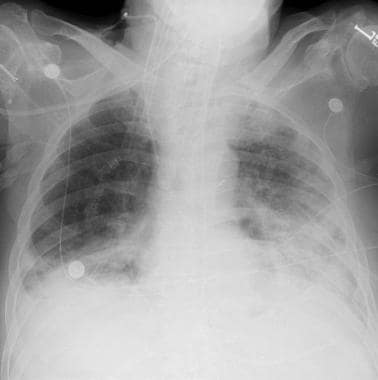
The acellular lungs ventilated with PEEP 4, 8 and 12 showed pulmonary rupture at lower IV when compared with cellular ones (300cc vs. 300cc respectively) On the other hand, lungs ventilated with PEEP 4 cmH 2O reached the highest IV (400cc), in addition, they showed the lowest elevations of Pap and FFR. Lungs ventilated with PEEP 8 and 12 suffered pulmonary rupture at lower IV (200cc and 150cc vs. We observed that lungs ventilated with PEEP 0 cmH 2O suffered pulmonary rupture at high IV (300cc), with significant increases of Pap (Pulmonary artery pressure) and FFR (Fluid filtration rate). This was done in blood perfused rabbit lungs and in lungs perfused with a Buffer-Albumin Solution. Forty-eight New Zealand rabbits (2.5-3.5 kg) were divided into four groups with PEEP settings of 0, 4, 8 and 12 cmH 2O, at increasing levels of inspiratory volume (IV). We aim to investigate the effect of several levels of PEEP on barotrauma and, whether an optimal level of PEEP exists. The use of Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) as a strategy of mechanical ventilation offers its advantages, such as improved oxygenation, without causing alveolar overstretching and barotrauma. Effect of using several levels of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure over barotraumas induced lung injury in a model of isolated and perfused rabbit lungs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
